Why Does Human Capital Management Matter?
The modern workplace has transformed dramatically. Organisations no longer view employees as mere resources but as valuable capital that drives innovation, productivity, and competitive advantage.
Human Capital Management (HCM) represents a strategic approach to managing people that focuses on maximising their potential throughout the entire employee lifecycle. Unlike traditional HR practices, HCM treats employees as investments rather than costs.
In today’s competitive business environment, companies that excel in HCM gain significant advantages. They attract top talent, improve employee engagement, and achieve better business outcomes through strategic people management.
This comprehensive guide explores what HCM truly means, how it differs from traditional HR approaches, and why it’s become essential for Australian and New Zealand businesses seeking sustainable growth.
Whether you’re leading a small business or managing a large organisation, understanding HCM fundamentals will help you unlock your workforce’s full potential.
What is Human Capital Management (HCM) and How Has It Evolved?
What constitutes Human Capital Management (HCM)? HCM encompasses the knowledge, skills, experience, and competencies that employees bring to an organisation. It’s the collective value of your workforce’s abilities, creativity, and potential.
The evolution from traditional HR to strategic HCM reflects changing business needs. Traditional HR focused on administrative tasks like payroll processing and compliance management. Today’s HCM approach emphasises strategic value creation through people.
The difference between human resources and Human Capital Management (HCM) is fundamental. Resources are consumed; capital appreciates over time. When you invest in employee development, training, and engagement, you’re building capital that generates returns.
Knowledge workers bring expertise that directly impacts business outcomes. Skills development creates competitive advantages. Experience provides institutional memory and wisdom. Competencies enable innovation and problem-solving capabilities.
The economic value of Human Capital Management (HCM) is measurable. Companies with engaged workforces show 23% higher profitability and 18% higher productivity. This demonstrates how strategic people management translates into tangible business results.
Modern organisations recognise that their competitive edge often lies in their people’s capabilities. Technology can be replicated, but organisational knowledge and culture remain unique differentiators.
How Does HCM Differ from HRM and HRIS?
- Human Capital Management (HCM) takes a comprehensive, strategic approach to people management. It focuses on maximising employee potential and aligning workforce capabilities with business objectives. HCM emphasises long-term value creation through strategic talent development.
- Human Resource Management (HRM) traditionally centres on administrative and operational functions. HRM handles day-to-day people management tasks like recruitment, payroll, and policy enforcement. It’s more tactical than strategic in nature.
- Human Resource Information System (HRIS) provides data management and basic HR functions. HRIS platforms store employee information, process payroll, and manage basic HR workflows. They’re technology tools that support HR operations.
| Aspect | HCM | HRM | HRIS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Strategic value creation | Administrative efficiency | Data management |
| Scope | Entire employee lifecycle | Daily HR operations | Information processing |
| Approach | Investment mindset | Operational mindset | Technology-focused |
| Outcomes | Business transformation | Process compliance | Data accuracy |
Choosing the right approach depends on your organisation’s maturity and objectives. Small businesses might start with HRIS basics, progress to HRM efficiency, then evolve toward strategic HCM thinking.
What Are the Core Components of Human Capital Management (HCM)?
1. Talent Acquisition and Recruitment
Strategic workforce planning forms the foundation of effective talent acquisition. This involves forecasting future skills needs, identifying talent gaps, and developing acquisition strategies that support business growth.
Employer branding attracts quality candidates by showcasing your organisation’s culture, values, and employee value proposition. A strong employer brand reduces recruitment costs and improves candidate quality.
Effective recruitment strategies utilise multiple channels including job boards, social media, employee referrals, and professional networks. Modern approaches emphasise candidate experience and relationship building.
Selection processes should be fair, efficient, and predictive. Structured interviews, skills assessments, and cultural fit evaluations help identify candidates who’ll succeed and stay long-term.
Streamlined hiring and onboarding processes, like those offered through integrated HR management platforms, reduce time-to-productivity and improve new employee experiences.
2. Employee Development and Training
Skills gap analysis identifies differences between current capabilities and future requirements. This strategic assessment guides training investments and development priorities.
Learning and development programs should be continuous and personalised. They might include formal training, mentoring, job rotations, and stretch assignments that build capabilities.
Career pathing and succession planning helps employees visualise their futures while ensuring organisational continuity. Clear development pathways improve engagement and retention.
Building a continuous learning culture encourages knowledge sharing, innovation, and adaptability. Modern learning management systems make training accessible and trackable.
Leadership development programs cultivate future leaders and strengthen organisational capability at all levels.
3. Performance Management and Employee Enablement
Goal setting and alignment ensure individual contributions support organisational objectives. Clear, measurable goals provide direction and motivation for employees.
Regular feedback and coaching replace annual reviews with ongoing development conversations. This approach improves performance and strengthens manager-employee relationships.
Performance evaluation systems should be fair, transparent, and focused on development rather than assessment. They help identify high performers and improvement opportunities.
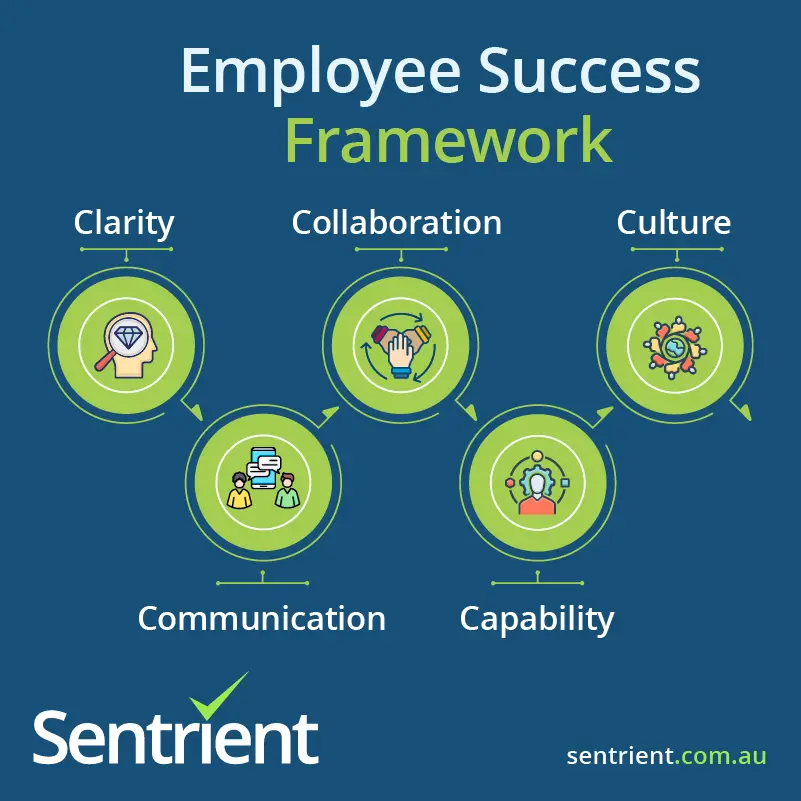
The 5 C’s framework encompasses five critical elements for employee success:
- Contribution – Meaningful work that creates value
- Capabilities – Skills development and learning opportunities
- Career – Clear growth paths and advancement prospects
- Connections – Relationships and networking within the organisation
- Compensation – Fair rewards and recognition systems
Performance improvement plans provide structured support for struggling employees while protecting organisational standards.
4. Compensation and Benefits
Total rewards philosophy goes beyond salary to include benefits, recognition, development opportunities, and work environment. This holistic approach attracts and retains talent effectively.
Salary benchmarking ensures competitive compensation whilst maintaining internal equity. Regular market analysis keeps compensation strategies current and fair.
Incentive programs and bonuses should align with business objectives and individual performance. Well-designed incentives motivate desired behaviours and outcomes.
Benefits packages must reflect employee needs and preferences. Modern benefits might include flexible work arrangements, wellness programs, and professional development allowances.
Fair compensation strategies build trust and reduce turnover whilst supporting business sustainability.
5. Employee Engagement and Experience
Employee experience optimisation focuses on every touchpoint in the employment journey. From recruitment through exit, each interaction shapes employee perceptions and engagement levels.
Engagement measurement through surveys and feedback tools provides insights into employee sentiment and areas for improvement.
Recognition and rewards programs celebrate achievements and reinforce desired behaviours. Both formal and informal recognition contribute to positive workplace culture.
Work-life balance initiatives support employee wellbeing and productivity. Flexible work arrangements, wellness programs, and time-off policies show genuine care for employees.
Building internal networks and connections helps employees feel valued and integrated into the organisational community.
How Do You Align Human Capital Management (HCM) with Business Strategy?
1. Linking HCM to Business Objectives
Aligning people strategy with business strategy ensures HCM investments support organisational goals. This alignment requires understanding business priorities and translating them into people management practices.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) for HCM should measure both leading and lagging indicators. Examples include employee engagement scores, retention rates, time-to-productivity, and talent pipeline strength.
Return on investment (ROI) in human capital can be calculated through metrics like revenue per employee, profit margins, and productivity improvements.
These measurements justify HCM investments and guide future decisions.
2. Organisational Culture and Values
Building and maintaining company culture requires intentional effort and consistent reinforcement. Culture shapes behaviour, decision-making, and employee experience throughout the organisation.
Values-based hiring and management ensures cultural fit whilst promoting diversity and inclusion. This approach reduces turnover and improves team cohesion.
Cultural transformation initiatives may be necessary when organisations evolve or face changing market conditions. Successful transformation requires leadership commitment and employee engagement.
What Are the Key Benefits of Human Capital Management (HCM)?
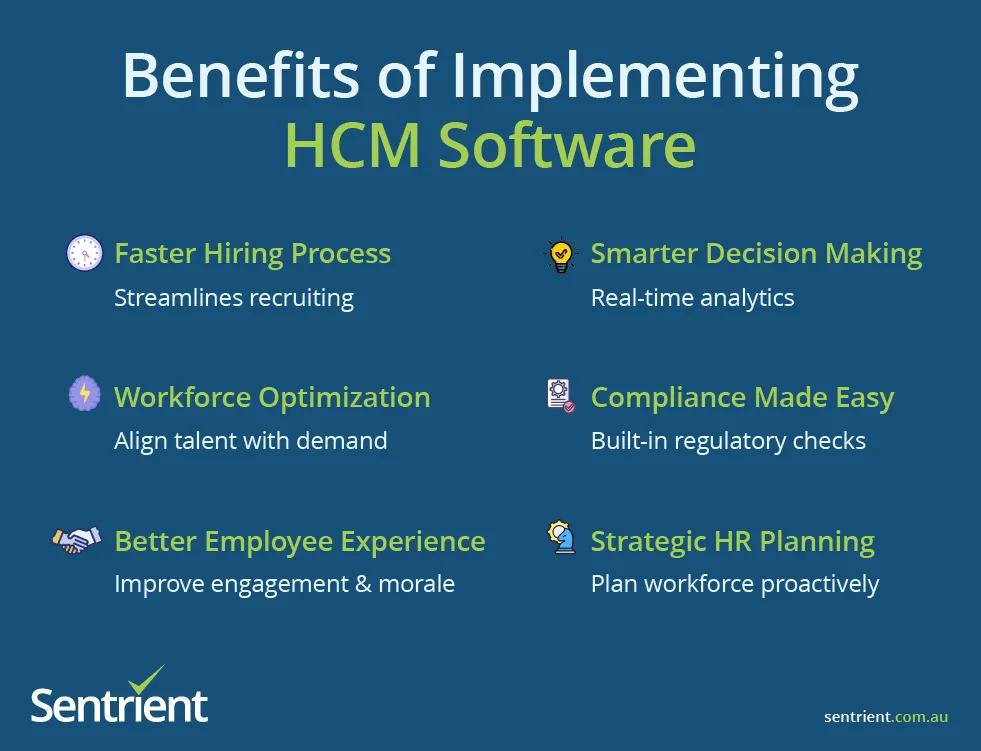
- Data-driven decision making – Gain insights into workforce trends and performance patterns
- Enhanced growth and scalability – Build adaptable workforces that drive innovation
- Improved talent attraction and retention – Create compelling employee value propositions
- Increased profits and productivity – Achieve 23% higher profitability through engagement
- Better data security – Implement proper access controls and compliance training
- Regulatory compliance – Meet legal obligations through systematic management
- Superior employee experience – Create positive workplace cultures that drive performance
Enhanced employee experience and engagement create positive workplace cultures that attract talent and improve performance. Satisfied employees become brand ambassadors and drive customer satisfaction.
What Are the Common Human Capital Management (HCM) Challenges and Solutions?
1. Operational Challenges
Talent strategy and skills shortages require proactive workforce planning and development. Organisations must build skills internally whilst competing for external talent in tight labour markets.
User experience and technology adoption challenges arise when HCM systems are complex or poorly designed. Modern platforms prioritise user-friendly interfaces and mobile accessibility.
Administrative burdens and manual processes reduce HR efficiency and increase errors. Automation through integrated HCM software solutions eliminates repetitive tasks and improves accuracy.
Systems integration complexities occur when organisations use multiple disconnected platforms. Unified HCM solutions or well-integrated systems reduce these complications.
Data security and privacy concerns require robust security measures and compliance protocols. Comprehensive GRC systems help organisations protect sensitive information whilst maintaining operational efficiency.
2. Strategic Challenges
Generational differences in the workforce require flexible management approaches. Different generations have varying communication preferences, career expectations, and technology comfort levels.
Remote work and hybrid model management presents new challenges for engagement, collaboration, and performance management. HCM strategies must evolve to support distributed workforces effectively.
Compliance and regulatory requirements continue expanding, particularly in areas like workplace safety, privacy, and employment law. Systematic compliance management becomes essential for risk mitigation.
Change management and organisational transitions require careful people management. HCM practices must support employees through uncertainty whilst maintaining productivity and engagement.
Workforce planning and forecasting become more complex in rapidly changing business environments. Advanced analytics and scenario planning help organisations prepare for various futures.
What Are the Four Pillars of Human Capital Management (HCM) Best Practices?
Successful HCM implementation relies on four fundamental pillars:
- Alignment – Connect HCM strategy with business goals through clear objectives
- Automation – Leverage technology for efficiency whilst maintaining human connection
- Communication – Build transparent, trust-based cultures through open dialogue
- Personalisation – Tailor approaches to individual employee needs and preferences
These pillars work together to create comprehensive HCM strategies that deliver sustainable results for both employees and organisations.
How Does Technology Transform Human Capital Management (HCM)?
1. HR Information Systems (HRIS) and HCM Software
Core HR technology platforms centralise employee data and automate routine processes. Modern systems integrate recruitment, onboarding, performance management, and compliance functions in unified platforms.
Employee self-service portals empower workers to manage their own information, request time off, and access company resources. This reduces administrative burden whilst improving employee experience.
Data management and analytics capabilities transform raw information into actionable insights. Advanced reporting helps organisations identify trends, predict outcomes, and make informed decisions.
Cloud-based solutions offer scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness compared to on-premises alternatives. They enable remote access whilst reducing IT infrastructure requirements.
Best-of-breed versus unified solutions present different advantages. Unified platforms like Sentrient’s integrated HR and compliance system offer seamless data flow and simplified management.
2. AI and Predictive Analytics in HCM
AI in recruitment and candidate screening improves efficiency and reduces bias. Machine learning algorithms can identify qualified candidates faster whilst promoting diversity and inclusion.
Predictive analytics for employee retention help organisations identify flight risks before they leave. Early intervention strategies can address concerns and improve retention rates.
Automated performance tracking and feedback provide continuous insights into employee productivity and engagement. Real-time data enables timely interventions and support.
Data-driven decision making for strategic planning uses historical patterns and predictive models to guide future HCM investments and strategies.
Identifying growth opportunities through analytics reveals skill gaps, development needs, and succession planning requirements that support business expansion.
3. Emerging Technologies
Mobile applications and digital experiences make HCM tools accessible anywhere, anytime. Modern workforces expect technology that supports flexible work arrangements and instant access.
Automation in HR processes eliminates manual tasks whilst improving accuracy and compliance. From payroll processing to incident reporting, automation reduces errors and saves time.
Integration with enterprise systems ensures data consistency and workflow efficiency across the organisation. Seamless connections between HCM and other business systems improve overall operations.
Real-time collaboration tools support team communication and project management, particularly important for remote and hybrid workforces.
How Do You Optimise Workforce Management?
1. Workforce Planning and Analytics
Strategic workforce planning models help organisations anticipate future people needs and develop acquisition or development strategies. This proactive approach prevents talent shortages and skills gaps.
Skills gap identification and forecasting guide training investments and recruitment priorities. Understanding capability needs enables targeted development programs.
Attrition, prediction and prevention use data analytics to identify retention risks and implement interventions. Proactive retention strategies are more cost-effective than reactive recruitment.
Optimal workforce deployment strategies ensure the right people work on the right projects at the right time. Effective deployment maximises productivity whilst supporting employee development.
2. Time, Attendance, and Compliance Management
Automated time-tracking systems improve accuracy whilst reducing administrative burden. Integration with payroll systems ensures consistent and compliant compensation processing.
Attendance monitoring and absenteeism trends help identify patterns that might indicate engagement issues or workplace problems requiring attention.
Regulatory compliance and labour law adherence become easier with systematic tracking and reporting. Compliance management systems help organisations meet their legal obligations consistently.
Payroll processing accuracy improves through integrated systems that eliminate manual data entry and calculation errors.
3. Employee Experience Enhancement
Consistent feedback and recognition systems create positive workplace cultures. Regular acknowledgement of contributions improves engagement and motivates continued performance.
Flexible work arrangements support work-life balance whilst maintaining productivity. Modern workforce expectations include location and schedule flexibility where possible.
Career development opportunities retain talent whilst building organisational capability. Clear development paths and learning opportunities engage employees in their long-term futures.
How Do You Measure Human Capital Management (HCM) Effectiveness?
1. HR Metrics and Analytics
Employee turnover rates indicate engagement levels and management effectiveness. High turnover suggests problems requiring investigation and intervention.
Time-to-hire and cost-per-hire metrics measure recruitment efficiency. These indicators help optimise hiring processes and resource allocation.
Employee satisfaction scores provide insights into workplace culture and management effectiveness. Regular surveys identify improvement opportunities and track progress over time.
Productivity and performance metrics link people management to business outcomes. These measurements demonstrate HCM value and guide improvement strategies.
2. HCM Return On Investment (ROI)
Calculating return on HCM investment requires comparing costs against benefits. Training investments should generate measurable improvements in performance or capability.
Cost-benefit analysis of HR programs helps prioritise investments and justify expenditure. This analysis ensures HCM budgets focus on high-impact initiatives.
Benchmarking against industry standards provides context for performance evaluation. External comparisons help organisations understand their relative HCM effectiveness.
Performance measurement should consider both quantitative metrics and qualitative indicators like employee engagement and cultural health.
What Are the Future Trends in Human Capital Management (HCM)?
1. Evolving Workplace Models
Remote and hybrid work arrangements require new management approaches and technology solutions. HCM strategies must adapt to support distributed workforces effectively.
Gig economy and flexible workforce models create new challenges for engagement and development. Organisations need strategies for managing diverse employment relationships.
Skills-based hiring and career mobility focus on capabilities rather than traditional job descriptions. This approach promotes internal mobility and career flexibility.
2. Technology Advancements
AI and machine learning applications will continue expanding in recruitment, performance management, and predictive analytics.
These technologies improve efficiency whilst enabling more personalised approaches.
Virtual reality in training and development offers immersive learning experiences. VR technology can simulate complex scenarios safely and cost-effectively.
Blockchain in credential verification could streamline hiring processes whilst reducing fraud. Verified qualifications and experience records improve recruitment accuracy.
3. Societal and Demographic Shifts
Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) focus continues growing in importance. HCM strategies must actively promote fairness whilst leveraging diverse perspectives for innovation.
Multi-generational workforce management requires understanding different values, communication styles, and career expectations across age groups.
Sustainability and social responsibility increasingly influence employer branding and employee engagement. Modern workers seek purpose-driven organisations aligned with their values.
How Do You Get Started with Human Capital Management (HCM) Implementation?
1. Assessment and Planning
Current state analysis identifies existing strengths and improvement opportunities. This assessment provides baseline understanding and guides implementation priorities.
Gap identification compares current capabilities with desired outcomes. Understanding gaps helps prioritise investments and develop realistic timelines.
Strategic planning processes should involve stakeholders across the organisation. Successful HCM implementation requires buy-in and support from leadership and employees.
2. Implementation Roadmap
Phased approach to HCM adoption reduces risks whilst building momentum. Starting with foundational elements and expanding gradually improves success rates.
Change management considerations include communication, training, and support for employees adapting to new systems and processes.
Resource allocation and budgeting must balance immediate needs with long-term objectives. Realistic budgets ensure sustainable implementation and ongoing success.
3. Measuring Success
Setting baseline metrics enables progress tracking and impact measurement. Clear success criteria guide implementation decisions and demonstrate value.
Regular monitoring and evaluation identify adjustment needs and improvement opportunities. Continuous assessment ensures HCM strategies remain effective and relevant.
Continuous improvement cycles incorporate feedback and lessons learned into ongoing refinement. Successful HCM implementation never truly ends but evolves constantly.
Conclusion
Human Capital Management (HCM) represents a fundamental shift from traditional HR thinking to strategic people investment.
Understanding HCM fundamentals empowers organisations to unlock their workforce’s full potential and achieve sustainable competitive advantages.
The strategic imperative of effective HCM cannot be overstated in today’s competitive environment. Organisations that invest in comprehensive HCM practices gain measurable advantages through engaged, capable, and aligned workforces.
Why Choose Sentrient for Your HCM Journey?
Sentrient stands as Australia’s most reliable HR and compliance solution, trusted by over 1,000 businesses across Australia and New Zealand.
Our integrated platform combines HCM, compliance training, and GRC capabilities in one user-friendly system designed specifically for the Australian workplace.
With Sentrient, you get rapid deployment in minutes, not months. Our cloud-based platform includes pre-loaded compliance courses, automated workflows, and comprehensive reporting that keeps your business compliant whilst driving employee engagement.
From recruitment and onboarding to performance management and compliance tracking, Sentrient transforms how you manage your most valuable asset—your people.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between HCM and traditional HR?
HCM takes a strategic approach focused on maximising employee potential and aligning workforce capabilities with business objectives. Traditional HR typically focuses on administrative tasks and operational efficiency rather than strategic value creation.
2. How does HCM software improve business outcomes?
HCM software provides data-driven insights, automates routine processes, and enables strategic workforce planning. This leads to improved employee engagement, better retention rates, and increased productivity that directly impacts business performance.
3. What are the main challenges in implementing HCM?
Common challenges include resistance to change, technology adoption difficulties, skills gaps, and integration complexities. Success requires strong leadership commitment, comprehensive change management, and phased implementation approaches.
4. How do you measure the ROI of HCM investments?
ROI measurement includes metrics like reduced turnover costs, improved productivity, faster time-to-hire, and increased employee engagement scores. Calculate costs versus benefits whilst considering both quantitative and qualitative improvements.
5. What role does AI play in modern HCM?
AI enhances recruitment screening, enables predictive analytics for retention, automates routine tasks, and provides personalised employee experiences. It improves efficiency whilst enabling more strategic human decision-making.
6. How can small businesses benefit from HCM practices?
Small businesses gain competitive advantages through strategic talent management, improved employee experiences, and efficient processes. Cloud-based HCM solutions make sophisticated capabilities accessible without large IT investments.
7. What are the key features to look for in HCM software?
Essential features include integrated HR functions, compliance management, employee self-service, analytics and reporting, mobile accessibility, and scalability. Look for solutions that grow with your business needs.
8. How does HCM support remote and hybrid workforces?
HCM systems provide digital collaboration tools, performance tracking capabilities, virtual onboarding processes, and engagement measurement tools that maintain connection and productivity regardless of location.
9. What compliance considerations are important in HCM?
Key compliance areas include workplace safety, privacy protection, employment law adherence, and data security. Integrated compliance management systems help organisations meet regulatory requirements systematically.
10. How often should HCM strategies be reviewed and updated?
HCM strategies should be reviewed annually at a minimum, with quarterly check-ins on key metrics. Major business changes, regulatory updates, or workforce shifts may require more frequent adjustments to maintain effectiveness.





